Background
Large Language Models (LLMs) offer promising advances in mechanical and aerospace engineering applications. This project aimed to assess their potential in engineering tasks, taking into consideration data privacy, legal issues, and overall practicality. OpenAI’s GPT-4, with its high reasoning capabilities, has shown success in tasks like pair programming and copy editing. The model's ability to draft and conceptualize has been harnessed in larger projects such as literature review and vehicle conceptual design.
Approach
The approach involved comparing both closed-source and open-source LLMs, using external data to assist LLMs, fine-tuning the LLM with a specific corpus of documents, and implementing safety guardrails. For most tasks, OpenAI’s GPT-4 was used, accessed via the ChatGPT web interface, an API call to OpenAI, or an API call to a Microsoft Azure cloud instance of OpenAI.
Accomplishments
The project has demonstrated various use cases and promising projects. LLMs have proved effective in pair programming and teaching, particularly in popular subjects with large data availability. A literature review tool and a hypersonic vehicle conceptual design tool (Figure 1) were developed, combining the LLM's ability to conceptualize and draft with established software to provide grounded predictions. However, LLMs struggled with tasks involving large datasets, math (if not given access to other tools), obscure programming languages, rigorous physical reasoning, and summarizing complex documents.
Despite these challenges, LLMs can be applied to various engineering tasks today, with more applications expected in the near future. Building engineering software around or with the assistance of an LLM shows significant promise, although it may be challenging due to the non-deterministic nature of the technology.
The project team worked with ITC to set up an Azure instance of OpenAI’s GPT-4. This instance has data protections in place to allow the use of SwRI sensitive data, a major step forward in applying LLMs to everyday tasks at SwRI. The project team also provided feedback for SwRI-trained LLMs. While it would be a significant investment, an LLM trained on SwRI's institutional knowledge could offer unique insights and efficiencies.
The project has resulted in three accepted conference papers on disparate fields, namely hypersonic aircraft design, air traffic control monitoring, and satellite component ground testing.
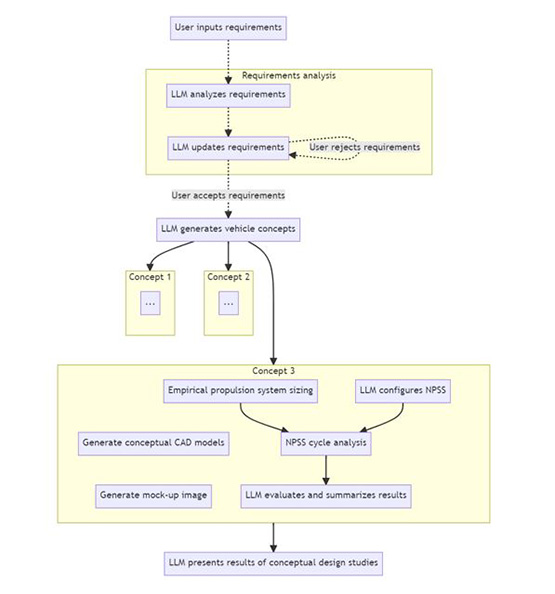
Figure 1: Notional process flow chart for hypersonic vehicle design tool
