Economic impacts from the pandemic and ongoing digital trends are expected to accelerate the adoption of digital manufacturing, also known as smart manufacturing. This means more U.S. companies will embrace “Industry 4.0” technologies that support agile workflows with robotics, automation, data analytics, and additive manufacturing.
This type of digital transformation can be challenging for even the largest manufacturers with established robotics programs and cybersecurity protocols. What does it mean for smaller manufacturers who may not have the culture or training to implement new technologies?
Southwest Research Institute is helping small- and medium-sized manufacturers (SMMs) ease the transition to smart manufacturing through the Texas Manufacturing Assistance Center (TMAC). For over 25 years, SwRI has helped industry by hosting the TMAC South-Central Region branch at our headquarters in San Antonio.
TMAC’s mission is to provide technical assistance and resources to help U.S. manufacturers grow and thrive. As part of the Manufacturing Extension Partnership (MEP), a National Institute of Standards and Technology-affiliated network of industry experts, TMAC is able to offer clients greater access to strategic support, guidance, process improvement, technical resources and advanced automation.
The MEP is a public-private partnership serving small- and medium-sized manufacturers in all 50 states and Puerto Rico. Image Courtesy of Manufacturing Extension Partnership (MEP).
What is Digital Manufacturing?
Digital manufacturing can integrate customer data with supply chain logistics to customize production using automation, machine learning, and collaborative robots while freeing humans from repetitive tasks. A main goal is to provide manufacturing companies with agile systems that can adjust for varying volumes or reconfigure operations more flexibly. COVID-19 demonstrated a need for smart, agile manufacturing to adjust for supply chain disruptions or the need to pivot to new products such as PPE. According to the MEP, digital manufacturing can reduce machine downtime by 30-50% or reduce time to market by 20-50%. Achieving these and other benefits, however, is challenging. Users need to understand which platforms best fit their application and implement technical training and resources to sustain the initial investment in automation and robotics technology.

Access the full digital manufacturing infographic here. Image Courtesy of Manufacturing Extension Partnership (MEP).
Through a recent grant, SwRI’s TMAC office now offers assistance to small manufacturers adopting digital manufacturing technologies such as industrial robotics and automation, cyber security, and additive manufacturing. These technologies are often ubiquitous in large manufacturing facilities across the country, but small and medium-sized manufacturers often have fewer dedicated resources and often less available capital, which slows adoption. The mission of this grant is to independently introduce and apply these technologies to the shop floor.
Collaborative Robot Applications for Digital Manufacturing
Collaborative robots, or cobots, can help enable digital manufacturing at small companies. Cobots, which operate near humans, are considered safer than traditional industrial robots. They can also be cost-effective when integrating automation into an assembly process. The TMAC South-Central Region office works closely with SwRI’s Collaborative Robot Laboratory to develop applications using software and machine vision that meet the unique demands of our customers.
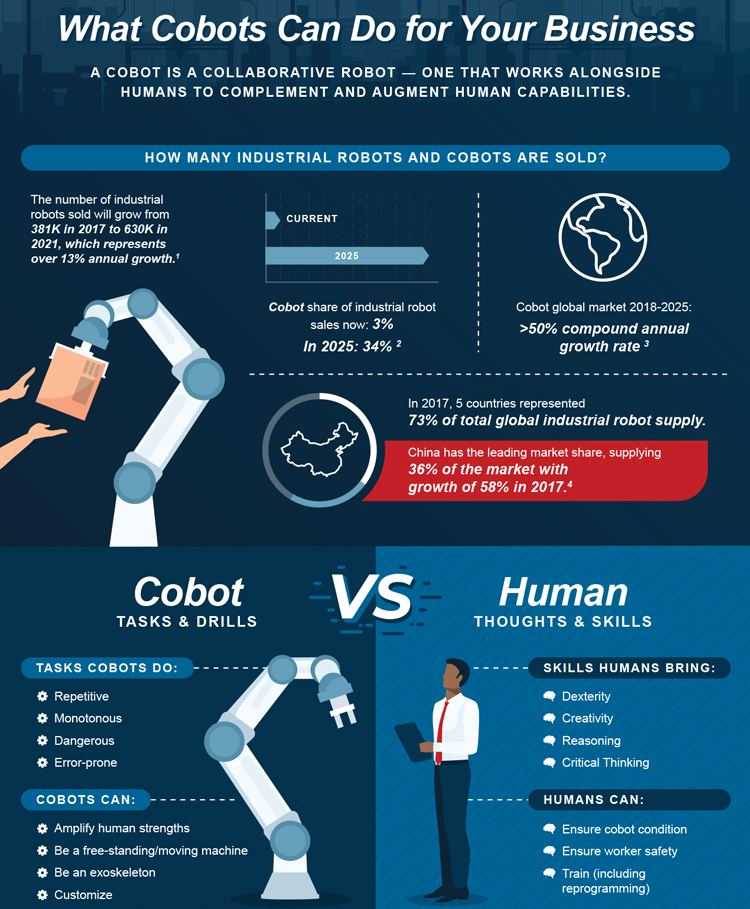
Learn more about collaborative robots here. Image Courtesy of Manufacturing Extension Partnership (MEP).
Assembling Traffic Safety Products with Collaborative Robots
The adoption of collaborative robots has dramatically increased in many different industries, which use them in a range of tasks. A Texas manufacturer of flexible traffic safety products came to TMAC to explore advanced manufacturing solutions, particularly if a collaborative robot could be deployed in their assembly work cells.

Example of traffic control device produced by TMAC customer.
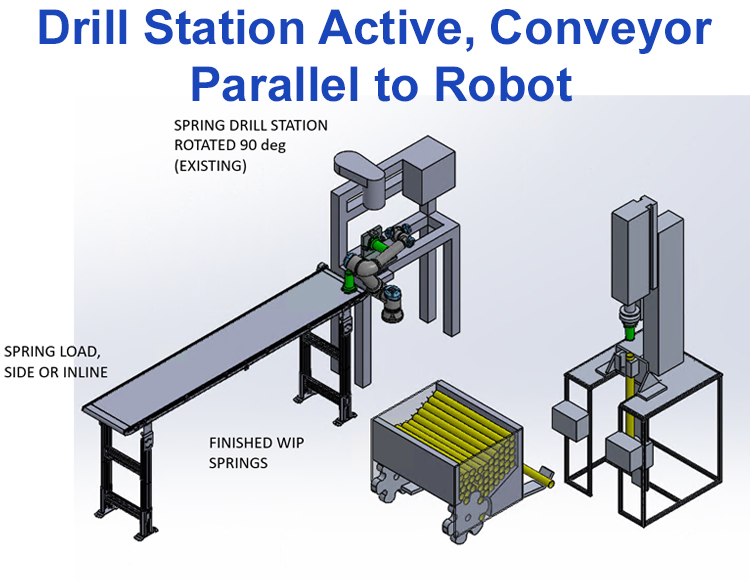
SwRI simulated a collaborative robot in the drill station for an assembly work cell that manufactures traffic control devices.
SwRI engineers assessed the feasibility of using cobots in the drill and weld station cells and developed layout configurations for review and consideration.
SwRI engineers then developed simulations to determine if the robot could keep up with the production. Because collaborative robots work side-by-side with operators, they are not as fast as traditional industrial robots, so throughput had to be verified. These simulations showed that collaborative robots could indeed keep pace with the production line.
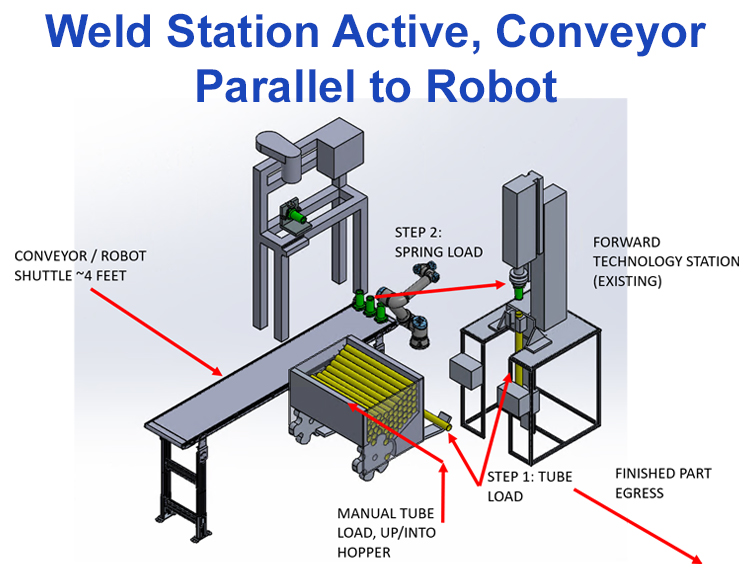
A simulation utilizes a collaborative robot in the weld station for manufacturing traffic control devices.
This company is making plans and setting directions to use robotics and automation to thrive and grow. Small and medium-sized manufacturers can leverage advanced automation and robotics to become more competitive and focus staff in other areas to support innovation and growth.
Robots are not just for large manufacturers. As robot orders continue to set records, the barrier to entry is not just cost. Small or medium-sized manufacturers wanting to explore where to best implement a cobot can contact their local MEP office. These experts can assess the opportunities, support planning, and guide integration.
TMAC and SwRI have the expertise and the domain knowledge to help implement impactful digital manufacturing solutions. We can support a range of needs and applications from strategy, concept development, and advanced solution integration.
Making the Case for Advanced Automation
The image below visualizes data from a 2015 survey of companies planning to implement digital manufacturing. Recent reports and white papers suggest the COVID-19 pandemic is already accelerating adoption of digital manufacturing.
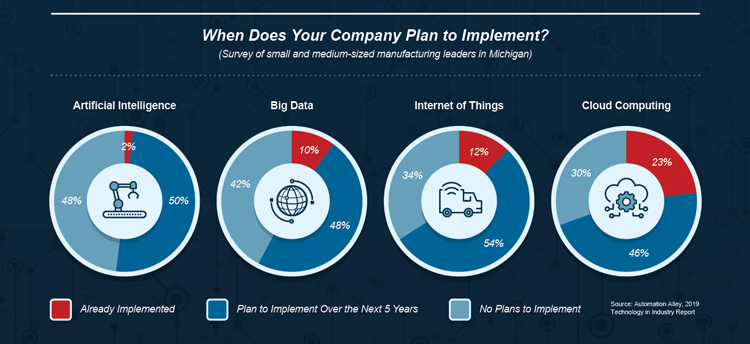
Image Courtesy of Manufacturing Extension Partnership (MEP).
If you are new to the process, and just getting started in collaborative robotics or digital manufacturing, here are some practical steps to set you on your journey:
Understand and quantify your goals (productivity, stability, throughput, etc.)
Create an automation roadmap and identify your candidate automation project.
Ensure your candidate process has been “leaned” out with a thorough review of the value stream. No need to automate waste!
Have an initial discussion with an expert/integrator about goals and approach.
Invite an expert/integrator to your facility to observe, process, and collect data.
Document your requirements, outline a scope of work, and obtain quotes.
Review range of solutions and cost and iterate to ensure goals are met.
Repeat the process with multiple solution providers if open to range of options.
Select a solution and/or integrator, and your journey begins.
Leverage your resources. Reach out to SwRI and TMAC. Check out the Robotics Industries Association, which maintains a wealth of information for manufacturers ranging from how to calculate your return on investment to ensuring safety in your workplace. Know that TMAC and SwRI are here for you and your company. Contact TMAC South-Central Region or watch our webinar on The Business Case for Advanced Automation, we are here to help.

